Create a CloudFront distribution
With CloudFront, Amazon created a CDN (Content Delivery Network), which can be used for serving static files in a fast manner. The actual files are being managed at one single place, but are provided by different servers. The particular server for a request is chosen based on the requester’s location. If a US-based client is requesting a static file from the CDN, the file is being provided by a server based somewhere in the USA. However, if the client’s location is Germany, the file won’t be served from a US-based, but a German server. This is done in order to save loading-time.
The servers, which hold a cached version of the static files are called Edge Locations. In the image below, each blue dot stands for at least one Edge Location. Some dots stand for up to 3 of them. More details about the AWS-Regions and Edge Locations can be found here.
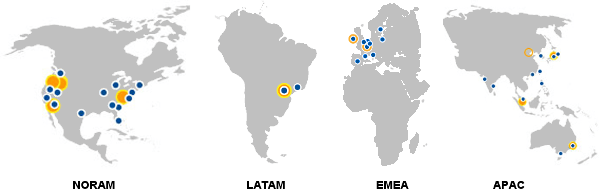
| Region | Country | City | ELs |
|---|---|---|---|
| NORAM | US | Ashburn, VA | 3 |
| NORAM | US | Atlanta, GA | 1 |
| NORAM | US | Dallas, TX | 2 |
| NORAM | US | Hayward, CA | 1 |
| NORAM | US | Jacksonville, FL | 1 |
| NORAM | US | Los Angeles | 2 |
| NORAM | US | Miami, FL | 1 |
| NORAM | US | New York, NY | 3 |
| NORAM | US | Newark, NJ | 1 |
| NORAM | US | Palo Alto, CA | 1 |
| NORAM | US | San Jose, CA | 1 |
| NORAM | US | Seattle, WA | 1 |
| NORAM | US | South Bend, IN | 1 |
| NORAM | US | St. Louis, MO | 1 |
| Region | Country | City | ELs |
|---|---|---|---|
| LATAM | BR | Rio de Janeiro | 1 |
| LATAM | BR | São Paulo | 1 |
| Region | Country | City | ELs |
|---|---|---|---|
| EMEA | NL | Amsterdam | 2 |
| EMEA | IE | Dublin | 1 |
| EMEA | DE | Frankfurt | 3 |
| EMEA | UK | London | 3 |
| EMEA | ES | Madrid | 1 |
| EMEA | FR | Marseilles | 1 |
| EMEA | IT | Milan | 1 |
| EMEA | FR | Paris | 2 |
| EMEA | SE | Stockholm | 1 |
| EMEA | PL | Warsaw | 1 |
| Region | Country | City | ELs |
|---|---|---|---|
| APAC | IN | Chennai | 1 |
| APAC | CH | Hong Kong | 2 |
| APAC | PH | Manila | 1 |
| APAC | AU | Melbourne | 1 |
| APAC | IN | Mumbai | 1 |
| APAC | JP | Osaka | 1 |
| APAC | KR | Seoul | 2 |
| APAC | SG | Singapore | 2 |
| APAC | AU | Sydney | 1 |
| APAC | TW | Taipei | 1 |
| APAC | JP | Tokyo | 2 |
| Region | Edge Locations |
|---|---|
| NORAM | 20 |
| LATAM | 2 |
| EMEA | 16 |
| APAC | 15 |
| Total | 53 |
Create S3-bucket
The static files for the distribution need to be stored at some place. There are also other concepts like e.g. origin pull, but here I will focus on a S3-bucket. Therefore, you first need to create a S3-bucket. It’s a best practice to give the S3-bucket the same name as the domain-name we use later on.
$ aws s3 mb s3://aws-blog.ioWith the command above you can create a S3-bucket with the name aws-blog.io. Keep in mind, that a S3-bucket-name needs to be unique for the whole service and not only your account. The command below is used to delete the bucket, in case it’s not needed anymore. That statement contains a –force at the end, which means that S3 will delete the bucket, even it has content within it. I normally do include the force-option, because I already have decided to delete a bucket, even if it contains data.
$ aws s3 rb s3://aws-blog.io --forceFor the CloudFront-distribution to work properly, there needs to be some access-rights adjustments. With the following bucket-policy, a download of any file within that bucket is allowed for any user. For a more professional setup, this should get reducded to CloudFront-sources / Principals only.
Just edit the following JSON-statement accordingly and save it as bucket-policy.json. It actually can be named anything, but within this post I will reference it.
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Id": "Policy1431883602565",
"Statement": [
{
"Sid": "Stmt1431883600330",
"Effect": "Allow",
"Principal": "*",
"Action": "s3:GetObject",
"Resource": "arn:aws:s3:::aws-blog.io/*"
}
]
}Now that you have an adjusted bucket-policy, it needs to be applied on the bucket itself. This is done by using aws s3api, as stated in the command below.
$ aws s3api put-bucket-policy --bucket aws-blog.io --policy file://bucket-policy.jsonEverything is now setup from a S3-environment point-of-view. The only thing that’s missing is the actual data respectively the static files which later on should get served by CloudFront. With the next command, a local folder and a S3-bucket are getting synchronized. Here, the source is the local folder /home/flo/aws-blog.io/_site and the target is the s3-bucket aws-blog.io. Sources and targets can both be either local folders or S3-buckets. The –delete amendment will delete every file in the target, if it’s not existent within the source.
$ aws s3 sync /home/flo/aws-blog.io/_site s3://aws-blog.io/ --deleteSetup CloudFront-distribution
Create a web-distribution
During both creation-modes (Method 1 and Method 2), the following values in the JSON-statement need to get adjusted to your individual account:
- DistributionConfig.Origins.Items[*].Id
- DistributionConfig.Origins.Items[*].DomainName
- DistributionConfig.DefaultCacheBehaviour.TragetOriginId
- DistributionConfig.CallerReference (I normally set here the current timestamp, however it needs to be unique within all your previous AWS-API-calls)
- DistributionConfig.Aliases.Items[*]
If you chose Method 1, you need to specify more parameters, as we here generate a default-distribution-config with the command amendment –generate-cli-skeleton, whereas for Method 2 we use a pre-configured config-file.
Method 1
For this alternative of setting up a CloudFront-distribution, we need a software called jq, which helps editing json-files. It does make sense to install that software now, as we also need it later on.
$ sudo apt-get install jq$ aws cloudfront create-distribution --generate-cli-skeleton > /tmp/aws-blog.io-distribution.json
$ vi /tmp/aws-blog.io-distribution.json
$ cat /tmp/aws-blog.io-distribution.json | jq '. | .DistributionConfig' > /tmp/aws-blog.io-distribution-only-config.json
$ aws cloudfront create-distribution --distribution-config file:///tmp/aws-blog.io-distribution-only-config.jsonMethod 2
$ aws cloudfront create-distribution --cli-input-json '
> {
> "DistributionConfig": {
> "Comment": "",
> "CacheBehaviors": {
> "Quantity": 0
> },
> "Logging": {
> "Bucket": "",
> "Prefix": "",
> "Enabled": false,
> "IncludeCookies": false
> },
> "Origins": {
> "Items": [
> {
> "OriginPath": "",
> "CustomOriginConfig": {
> "OriginProtocolPolicy": "http-only",
> "HTTPPort": 80,
> "HTTPSPort": 443
> },
> "Id": "custom-aws-blog.io.s3-website.eu-central-1.amazonaws.com",
> "DomainName": "aws-blog.io.s3-website.eu-central-1.amazonaws.com"
> }
> ],
> "Quantity": 1
> },
> "DefaultRootObject": "index.html",
> "PriceClass": "PriceClass_All",
> "Enabled": true,
> "DefaultCacheBehavior": {
> "TrustedSigners": {
> "Enabled": false,
> "Quantity": 0
> },
> "TargetOriginId": "custom-aws-blog.io.s3-website.eu-central-1.amazonaws.com",
> "ViewerProtocolPolicy": "allow-all",
> "ForwardedValues": {
> "Headers": {
> "Quantity": 0
> },
> "Cookies": {
> "Forward": "none"
> },
> "QueryString": false
> },
> "SmoothStreaming": false,
> "AllowedMethods": {
> "Items": [
> "GET",
> "HEAD"
> ],
> "CachedMethods": {
> "Items": [
> "GET",
> "HEAD"
> ],
> "Quantity": 2
},
> "Quantity": 2
> },
> "MinTTL": 0
> },
> "CallerReference": "Mon May 25 21:39:53 CEST 2015",
> "CustomErrorResponses": {
> "Quantity": 0
> },
> "Restrictions": {
> "GeoRestriction": {
> "RestrictionType": "none",
> "Quantity": 0
> }
> },
> "Aliases": {
> "Items": [
> "aws-blog.io"
> ],
> "Quantity": 1
> }
> }
> }
> 'Creating a DNS-record for distribution
This setup is intended for domains hosted within Route53. It’s also possible with other hosters. There you just need to create a CNAME for your distributions DNS-name. If you don’t have a domain within Route53 yet, there’s already a blog-post on who to set that up. You can find that post here. For the creation of the CNAME-DNS entries, it’s advised to wait until the status of the distribution has changed from In Progress to Deployed. The state of all distributions can be checked with aws cloudfront list-distributions, as described below.
$ aws cloudfront list-distributions --query "DistributionList.Items[*].{Domain: join(', ', Aliases.Items), DistributionID: Id, Status: Status, CloudFrontDomain: DomainName}" --output tableYou then can create a file called aws-blog.io-cloudfront-alias.json (you actually can name it anything, but I’ll reference it later on), copy & paste the following JSON-statement and edit accordingly. The mentioned DNSName of the distribution is also in the command above, which you just used to check the distribution’s state.
NOTE: The HostedZoneId in AliasTarget is AWS’s HostedZoneId of CloudFront, so you need so set that specific one with the ID Z2FDTNDATAQYW2 and not your own one.
{
"Comment": "CloudFront CNAME",
"Changes": [
{
"Action": "CREATE",
"ResourceRecordSet": {
"Name": "aws-blog.io",
"Type": "A",
"AliasTarget": {
"HostedZoneId" : "Z2FDTNDATAQYW2",
"DNSName": "d2bpXXXXXztnay.cloudfront.net",
"EvaluateTargetHealth": false
}
}
}
]
}The previously created JSON-statement gets used as a parameter for the next command. The only other unique parameter is the hosted-zone-id.
$ aws route53 list-hosted-zones --query "HostedZones[*].{Name: Name, FullID: Id"}
$ aws route53 change-resource-record-sets --hosted-zone-id Z3GXXXXXXGTO --change-batch file://aws-blog.io-cloudfront-alias.json$ sudo apt-get install jq$ cat /tmp/aws-blog.io-distribution.json | jq '. | .DistributionConfig' > /tmp/aws-blog.io-distribution-only-config.json
$ aws cloudfront create-distribution --distribution-config file:///tmp/aws-blog.io-distribution-only-config.json$ aws cloudfront list-distributions --query "DistributionList.Items[*].{Domain: join(', ', Aliases.Items), DistributionID: Id, Status: Status}" --output table
-------------------------------------------------------
| ListDistributions |
+-----------------+-----------------------+-----------+
| DistributionID | Domain | Status |
+-----------------+-----------------------+-----------+
| E2NGXXXXXBI7IC | aws-blog.io | Deployed |
| E190XXXXXL0LJU | staging.aws-blog.io | Deployed |
+-----------------+-----------------------+-----------+Delete distribution
In order to delete a distribution, it first needs to get in a disabled-state. After this step had been done, it can get deleted.
For a more easy way of editing JSON-files, the software json (formerly known as json-tools) and jq is being installed.
$ sudo npm install -g json
$ sudo apt-get install jqAfter the installation of the mentioned tools, you can download the current distribution-config and set enabled: false in it. This is all done with the next command-block. The only parameter that needs to get adjusted is the –id, which you can get with a listing of all domains as previously done. For the update-process you need the value of ETag, which will be listed with the very first command.
$ aws cloudfront get-distribution-config --id E3GXXXXXXSPXOX --query "{ETag: ETag}"
$ aws cloudfront get-distribution-config --id E3GXXXXXXSPXOX | jq '. | .DistributionConfig' > /tmp/aws-blog.io-distribution.json
$ cat aws-blog.io-distribution.json | json -e 'this.Enabled=false' > aws-blog.io-distribution-disabled.json
$ aws cloudfront update-distribution --id E3GXXXXXXSPXOX --if-match E2IPXXXXXXWKX0 --distribution-config file:///tmp/aws-blog.io-distribution-disabled.jsonThe status of the distribution needs to be Deployed, in order to proceed. You can always check the status of all of your distributions with the following command, which just lists all distributions and their states.
$ aws cloudfront list-distributions --query "DistributionList.Items[*].{Domain: join(', ', Aliases.Items), DistributionID: Id, Status: Status}" --output tableWhen the state of the distribution has changed to Deployed, you can trigger the actual deletion with the following command.
$ aws cloudfront delete-distribution --id E3GXXXXXXXSPXOX --if-match E2IPXXXXXXWKX0Invalidations
An invalidations is always needed, when a file has been adjusted before it’s specified expiration-date. When an invalidation is triggered in CloudFront, all cached versions of the files on all Edge Locations are getting renewed. Big websites with many deployments should rather look into an asset-pipeline concept with hashes as filenames, because after 1.000 invalidations per month, you will get charged for it.
NOTE: An invalidation call like the one below needs an unique CallerReference. That one needs to be specific for all calls to the AWS-API. As I actually don’t use the CallerReference, I just set a current timestamp for it.
$ invalidation_batch='{"Paths": {"Quantity": 1,"Items": ["/*"]},"CallerReference": "'`LC_ALL=en_US.UTF-8 date`'"}'
$ aws cloudfront create-invalidation --distribution-id E190XXXXXL0LJU --invalidation-batch "$invalidation_batch"